Hair Transplant
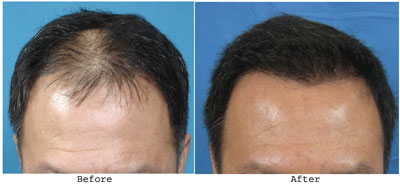
Hair transplantation refers to a surgical technique by which individual hair follicles are extracted from a particular region in body known as the 'donor site' and transplanted in to a bald or balding part known as the 'recipient site'. Hair transplant is a minimally invasive procedure essentially used to treat male pattern baldness. In this procedure, grafts, which contain hair follicles that are genetically resistant to balding, are transplanted to the balded scalp. Hair transplantation can also be used to restore eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair and chest hair and to cover the deep scars caused due to accidents or surgery such as face-lifts and previous hair transplants.
In hair transplantation, grafts contain almost all of the epidermis and dermis that surrounds the hair follicle. Moreover, tiny grafts are transplanted into the bald scalp rather than a single strip of skin.
Donor hair can be harvested two ways namely Strip harvesting and Follicular unit extraction
Strip harvesting
In this procedure, a strip of scalp tissue is removed and the wound is sutured together. The grafts or pieces of scalp tissue which is cut into small pieces are then transplanted into the recipient sites i.e. in the thinning region in the patient's scalp. This procedure could leave a "pencil thin" linear scar in the donor region, which is generally covered by a patient's hair. The recovery period takes around 2 weeks. The stitches/staples will be removed by medical personnel or sub cuticular suturing.
Follicular unit extraction or FUE Harvesting
In this procedure, individual follicular units that contain 1 to 4 hairs are removed. This micro removal generally uses small punches between 0.6mm and 1.0mm in diameter. Each of the hair follicles is inserted into small recipient sites made by the surgeon with the help of a placement tool. As only individual follicles are removed, small, punctate scars might remain after the surgery and post-surgical pain is significantly reduced. Recovery from FUE usually happens within 7 days.
Surgery
Hair transplant operations are usually performed on an outpatient basis, under mild sedation (optional) and local anesthesia, which generally lasts about six hours. The scalp is shampooed and then treated using an antibacterial agent.
In the follicular unit procedure, the doctor or surgeon harvests a strip of skin from the posterior scalp, from a region that has good hair growth. The strip is usually about 1-1.5 x 15-30 cm in size. Individual follicular unit grafts are then dissected from the strip. Using binocular stereo-microscopes, excess fibrous and fatty tissue are removed. The most advanced method of closure is called 'Trichophytic closure' and results in finer scars at the donor region. FUE harvesting can provide natural results with no conspicuous scarring.
The surgeon then employs micro blades or fine needles to puncture the sites for transplanting the grafts. They position the grafts in a predetermined density and pattern, and angle the wounds in a particularly consistent fashion to create a natural hair pattern.
Post-operative care
Semi-permeable dressing, which facilitates seepage of blood and tissue fluid, must be applied and changed every day. The recipient region must be protected from exposure to sunlight, and shampooing is started two days following the surgery. Shampooing is very important as it prevents scabs from occurring around the hair shaft. Scabs, which attach to the hair shaft, often enhance the risk of losing newly transplanted hair follicles during the first 7 to 10 days after the surgery.
For the first ten days, all the transplanted hairs, due to their sudden relocation, tend to fall out. However, after two to three months, new hair begins to grow from the moved follicles. The patient's hair will grow in its normal course, and will continue to thicken during the next six to nine months.